Retinol and Bio-Retinol: The Dynamic Anti-Aging Skincare Duo
Fact checked
By Azrung Fayaz, Doctor of Internal Medicine | MBBS, FCPS, MRCP
Last Updated on June 9th, 2025 / Published on October 23, 2023

Everyone wants to keep their youthful glow. The numbers say it all: the anti-aging market was worth $63 billion in 2022. By 2030, it might hit $106 billion.1 This significant jump shows how much we all care about our skin.
Doctors hail retinol as the top choice for anti-aging. But what is it exactly, and how does it help our skin? In this guide, we’ll break this down and address your concerns. You’ll also learn about bio-retinol. So, let’s dive in.
What Makes Retinol a Must-Have in Skincare?
Research shows that retinol boosts skin health. For example, one study2 found that 12 weeks of retinol use reduced wrinkles and dark spots. Another observed improved skin hydration and fewer wrinkles in just seven weeks.3

What is Retinol?
Retinol, known as vitamin A1, is a natural compound. It is the most absorbed and potent form of vitaminA.
A glance at history reveals retinol’s age-old recognition. Over a century ago, doctors used it to treat night blindness.4 More recently, people have used it to relieve skin issues.
Where Does Retinol Come From?
Retinol comes from animal sources like liver, eggs, and dairy. Fruits and vegetables, like carrots, are also rich in retinol.5
Scientists can also make retinol in the lab using unique ingredients and processes.
How Does Retinol Work?
Once applied to your skin, retinol turns into retinoic acid. This active form communicates with skin cells, directing essential skin functions.
Specifically, it speeds up skin repair and reduces dark spots. Here’s how:
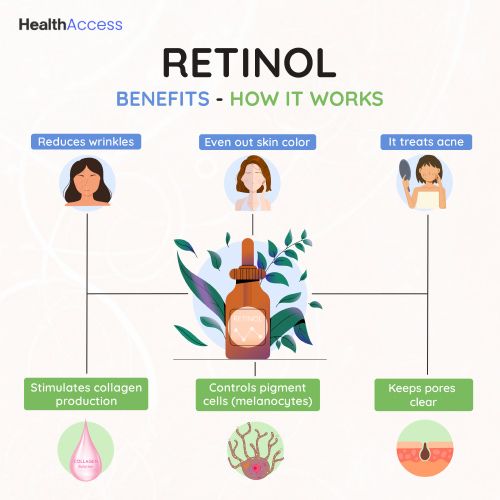
- Retinol triggers skin cells to make newer cells.6 This replaces older, worn-out skin.
- It stimulates the body to make more collagen.6 At the same time, retinol reduces collagen breakdown. The increased collagen keeps skin tight and young-looking.
- Retinol controls pigment cells (melanocytes).7 This helps maintain even skin tones.
- It treats acne by keeping pores clear.

What Are the Skin Benefits of Using Retinol?
Retinol has many research-proven skin benefits. It:
- Reduces wrinkles. For example, in one study,8 0.075% retinol smoothed out fine wrinkles in just four weeks. It also removed deeper wrinkles in 24 weeks.
- Evens out skin color. People using a 3% retinol peel every six weeks noticed fewer dark spots. Their skin also had smaller pores.9
- Keeps pores clear and tackles acne. Using 0.15% retinol for 12 weeks reduced acne scars in a study.10
When Should You Apply Retinol?
A New York skin doctor, Dr. Joshua Zeichner, recommends using retinol at night.
The sun can harm retinol-treated skin.11 So, by applying it at night, you can avoid red and sore skin.
Where Does Retinol Go in Your Skincare Routine?
For the best results, follow this retinol routine:
- Clean your face

- Tone (if you want)

- Put on retinol

- Wait 10 minutes

- Add moisturizer

- Use eye cream

- Always end with sunscreen

The Concerns You Might Have About Using Retinol
Now that we’ve explored retinol’s uses and advantages let’s tackle some frequent questions and concerns.
Why Does Retinol Make My Skin Peel?
When starting with retinol, you might notice your skin peeling. But don’t worry. It’s your skin removing old cells and making way for new ones.
Higher doses, like 1% retinol, cause more peeling than lower doses.12 So, if you feel your skin is dry, start with smaller amounts. Also, remember to moisturize and use sunscreen. This helps keep irritation away.
Can Retinol Darken My Skin?
Retinol brightens skin complexion. It does not darken it. For example, in one study,13 using 0.5% retinol cream reduced dark spots.
Is Retinol Dangerous for Skin Health?
Retinol is a trusted skincare ingredient. Most users can experience its benefits without any side effects. For this, it’s essential to use it the right way.
For example, avoid using it before stepping out into the sun. Otherwise, as discussed, this can lead to skin irritation. Likewise, using large quantities of retinol can cause excessive skin peeling or dryness.14
To avoid such complications, always follow your doctor’s advice and use retinol correctly.
Is Retinol Like Botox?
Both retinol and Botox tackle aging, but they are not the same. Here’s how they differ:
| Botox | Retinol | |
| Origin | A toxin from bacteria | Form of vitamin A from natural sources or made in the lab |
| Function | Paralyzes muscles | Alters skin genes |
| Duration | Lasts for months | Ongoing use needed |
| Safety Profile | Riskier | Safer |
What is Bio-Retinol?
Bio-retinol is a natural retinol alternative. It’s a plant-derived retinol from sources like carrot seed oil.
Bio-retinol acts like retinol and offers the same skin benefits. But given its plant-based origins, it’s milder and less prone to side effects than retinol.
What Are the Benefits of Using Bio-Retinol?
Bio-retinol has many skin benefits. Like retinol, bio-retinol:
- Smoothes skin
- Evens skin tone
- Boosts skin hydration
- Reduces wrinkles
These benefits are research-proven. For example, a study15 tested bio-retinol on 60 women. After four weeks, their skin looked brighter and smoother, with fewer wrinkles.
How Does Bio-Retinol Differ from Retinol?
| Bio-retinol | Retinol | |
| Tolerance | Better tolerated for sensitive skin | Maybe harsh for some people |
| Potency | Generally milder, less potent | Potent |
| Sun sensitivity | No | Yes |
| Pregnancy/breast-feeding | Safe | Use with caution |
| Environmental impact | Eco-friendly. Always sourced from natural sources | Synthetic production may have an environmental impact |
How Do You Choose Between Bio-Retinol and Retinol?
Choosing retinol or bio-retinol depends on your skin and needs. Here are general recommendations:
- Choose bio-retinol if you have sensitive skin or want to reduce dark spots.
- Pick retinol if you have tougher skin and want to help reduce the signs of aging.
For more personalized recommendations, please consult your skin doctor.
How Often Should You Apply Retinol or Bio-Retinol Products?
Use these products at night. Begin using them 2-3 times per week.
You can increase the frequency as your skin gets used to them.
What Combinations and Pairings Enhance Skincare?
Using retinol or bio-retinol with other ingredients can amplify benefits.
For example, you can combine retinol or bio-retinol with:
- Hyaluronic acid: A study16 showed this combination reduced wrinkles and improved skin health.

- Niacinamide: In a 12-week study,17 this combo increased retinol’s benefits and improved patient satisfaction.

- Vitamin C: This combination protects against environmental damage and reduces dark spots. It also boosts new cell production.

- Peptides: Together, they boost collagen production. This gives you younger, tighter skin.

Takeaway
Retinol is a powerhouse in skin care. Backed by studies, its benefits range from reducing wrinkles to improving skin tone. But it’s not for everyone, and that’s where bio-retinol steps in. The plant-based alternative offers a gentler approach with its own set of advantages.
Whether you choose retinol or bio-retinol, understanding how to use them is vital. So remember to consult your doctor before starting any new product.
Sources
- Hancock A. Anti Aging Market Size, Share, Trends, Opportunities Analysis Forecast Report by 2030. Published 1676100831000. https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/anti-aging-market-size-share-trends-opportunities-analysis-hancock. Accessed September 22, 2023
- Zasada M, Budzisz E, Erkiert-Polguj A. A Clinical Anti-Ageing Comparative Study of 0.3 and 0.5% Retinol Serums: A Clinically Controlled Trial. Skin Pharmacol Physiol. 2020;33(2). doi:10.1159/000508168
- Zasada M, Drożdż Z, Erkiert-Polguj A, Budzisz E. A blinded study assessment of the efficacy of an original formula with retinol in combination with sonophoresis. Dermatol Ther. 2020;33(1). doi:10.1111/dth.13163
- Chen G, Weiskirchen S, Weiskirchen R. Vitamin A: too good to be bad? Front Pharmacol. 2023;14. doi:10.3389/fphar.2023.1186336
- McEldrew EP, Lopez MJ, Milstein H. Vitamin A. Published online January 2023. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29493984/. Accessed September 22, 2023
- Zasada M, Budzisz E. Retinoids: active molecules influencing skin structure formation in cosmetic and dermatological treatments. Advances in Dermatology and Allergology/Postȩpy Dermatologii i Alergologii. 2019;36(4):392.
- Alfredo MG, Maribel PM, Eloy PR, Susana GE, Luis LGS, Carmen GM. Depigmenting topical therapy based on a synergistic combination of compounds targeting the key pathways involved in melasma pathophysiology. Exp Dermatol. 2023;32(5). doi:10.1111/exd.14752
- Spierings NMK. Evidence for the Efficacy of Over-the-counter Vitamin A Cosmetic Products in the Improvement of Facial Skin Aging: A Systematic Review. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2021;14(9):33.
- Sadick N, Edison BL, John G, Bohnert KL, Green B. An Advanced, Physician-Strength Retinol Peel Improves Signs of Aging and Acne Across a Range of Skin Types Including Melasma and Skin of Color. J Drugs Dermatol. 2019;18(9). https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31524348/. Accessed September 22, 2023
- Callender VD, Baldwin H, Cook-Bolden FE, Alexis AF, Gold LS, Guenin E. Effects of Topical Retinoids on Acne and Post-inflammatory Hyperpigmentation in Patients with Skin of Color: A Clinical Review and Implications for Practice. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2022;23(1):69.
- Tolaymat L, Dearborn H, Zito PM. Adapalene. In: StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing; 2023.
- Mellody KT, Bradley EJ, Mambwe B, Cotterell LF, Kiss O, Halai P, et al. Multifaceted amelioration of cutaneous photoageing by (0.3%) retinol. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2022;44(6):625.
- Dhaliwal S, Rybak I, Ellis SR, Notay M, Trivedi M, Burney W, et al. Prospective, randomized, double-blind assessment of topical bakuchiol and retinol for facial photoageing. Br J Dermatol. 2019;180(2). doi:10.1111/bjd.16918
- Zasada M, Budzisz E. Randomized parallel control trial checking the efficacy and impact of two concentrations of retinol in the original formula on the aging skin condition: Pilot study. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2020;19(2). doi:10.1111/jocd.13040
- Draelos ZD, Gunt H, Zeichner J, Levy S. Clinical Evaluation of a Nature-Based Bakuchiol Anti-Aging Moisturizer for Sensitive Skin. J Drugs Dermatol. 2020;19(12). doi:10.36849/JDD.2020.5522
- Li WH, Wong HK, Serrano J, Randhawa M, Kaur S, Southall, et al. Topical stabilized retinol treatment induces the expression of HAS genes and HA production in human skin in vitro and in vivo. Arch Dermatol Res. 2017;309(4). doi:10.1007/s00403-017-1723-6
- Handler M, Adams-Woodford A, Ayres P, Giancola G, Diaz I. Facial Aging Improvement Case Study Using a Novel Combination of Retinol, Niacinamide, and Terminalia Chebula. J Drugs Dermatol. 2022;21(7). doi:10.36849/JDD.6621





